Introduction
Last modification 04/04/2023
The evolution of Money
Barter System
- Characteristics:
- The most simple way of exchange
- Goods or services are exchanged against other good or services
- Functionality determined by hunter gatherer, humans on old ages
- Timespan:
- 98000 BC till 900BC
- Still practiced today in rare forms
- Examples:
- Fish against a wheat bag
- Mammoth against Axe
- Pros:
- Problem solving and exchange innovation
- No middle man needed
- Exchange by occupation
- Cons:
- Laborious
- No common measure of value
- Problems of storage
- Indivisibility of certain goods
- No sufficient store of value
Commodity Money
- Characteristics:
- As the barter system, cannot store value commodities that don't get foul were stored
- Commodities should be possible to store for a long time and be limited in quantity / quality
- Expensive and labor extensive store commodities such as salt
- Timespan:
- High phase 6000 BC till 500AD
- Still today a way to store value in commodities that do not get foul such as Oil and Grain
- Examples:
- Salt in Rome 80BC - 400AD)
- Tobacco in Virginia 1708 - 1860)
- Cattle in India, Sugar in Brazil, Rice in Carolina, Tea in Mongolia
- Pros:
- Better way to exchange value than barter
- Right measurement
- Cons:
- Space intensive
- No universal acceptability
Metal Money
- Characteristics:
- Humans found a better store as Metals and Precious Metals
- Already used for armors and tools
- Inherently valuable and scarce
- Gold backed IOUs: Goldsmiths stored gold to give people a share with which was exchange possible
- Legal tender coinage: first pressed money in coins (issue debasement)
- Timespan:
- High phase 600 BC till today
- Till today an determined way to store value and exchange also
- Examples:
- Ancient Greece, Lydians 600BC)
- 16th to 17th century Goldsmiths in England
- Pros:
- Scarce and Supply limited
- Solid
- Store of value valu measurement
- Cons:
- Debasement because mixed
Commodity Backed or Representative Money
- Characteristics:
- Occurred because gold and silver merchants or banks would issue receipts to their depositors, redeemable for the commodity money deposited
- These receipts became generally accepted as a means of payment and were used as money.
- The gold standard, a monetary system where the medium of exchange are paper notes that are convertible into pre-set, fixed quantities of gold, replaced the use of gold coins as currency in the 17th–19th centuries in Europe.
- Timespan:
- High phase 600 BC till today
- Banknotes were first issued in Europe by Stockholms Banco in 1661.
- Examples:
- Paper money or banknotes were first used in China during the Song dynasty.
- Pros:
- Fungible
- Durable
- Divisible
- Portable
- Acceptable
- Scarce
- Cons:
- Not credit
- Low liquidity
- Cannot cover externalities
Fiat Money
- Characteristics:
- Issued by central authority as the Central Bank
- Currency as a circulation medium to transport, exchange and store
- Measurement of value, however inflationary
- Timespan:
- 960AD till today
- Examples:
- 1690 AD in the US: Bills to credit
- US dollar issued by the FED
- EURO issued by the ECB
- Pros:
- Transportable
- Measurable
- Exchange measurement
- Cons:
- Inflationary
- Centralized
- Printed in mass especially in crisis times
Plastic Money
- Characteristics:
- As is difficult to store banknotes, banks invented plastic cards as debit/credit cards
- Account money has invented
- Storing of value just digitalized
- Timespan:
- 1946 AD till today
- Examples:
- First bank issued credit card in 1946 by Brooklyn banker
- Pros:
- Acceptability
- Storable
- Exchange measurement
- Trackeable
- Cons:
- Account money can be doubled by the payment provider
- Centralized
- Similar effects like fiat money
Cryptocurrencies
- Characteristics:
- Emerged as ultimate alternative to normal forms of money
- Blockchain technology
- Gives the issuer the possibility to design
- Double spending is not possible
- Timespan:
- 2008 till today
- Examples:
- Bitcoin BTC
- Ethereum TH
- Monero XMR
- Ripple XRP
- Pros:
- Decentralized
- Storable
- Scalable
- Exchange Measurement
- Store of Value
- Cons:
- Development is ongoing
The price formation machine
Negative Feedback System
A society with a good as money creates a Negative feedback System. This can be applied to Barter, Commodity Money and Metal Money. A society with a money which value can be traced back ("regressed") to its value as a commodity also creates a Negative feedback System. This can be applied to Representative Money.
A Negative feedback occurs when some function of the output of a system is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances..


A Negative feedback tends to reduce the effects of gain change but, in exchange, increases stability. A negative feedback system is a self regulation mechanism that helps maintain stability or balance in a system.
Characteristics
- Price formation follows marginal wishes of consumers
- Relative prices prioritize consumers wishes
- Resources are allocated according to consumers wishes.
- Entrepreneurs get fair signals about market demand
- Entrepreneurs assume the risk of their projects
- Companies are funded only by sales, according to consumers aggregated demand.
- Little entry barriers for new providers.
- New demand is always satisfied by providers.
- Values are freely chosen by citizens.
Problems
- Hoarding
- Externalities
- Critical Resources
- Money Scarcity
- The Problem of Credit
The abandoned road
Monetary Expansion
Central Planning
Scientifically planned society. Debate on neutrality of money, Normative vs positive economics

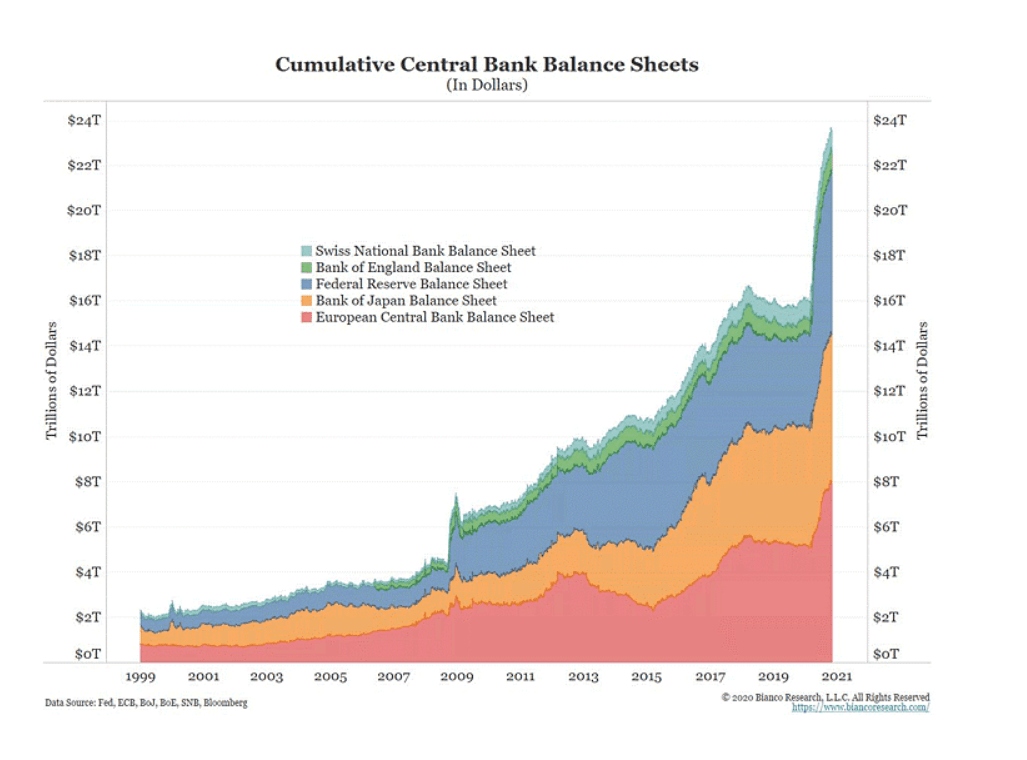
You can explore a more extended list of changes on this web.
Positive Feedback System
A society driven by monetary expansion is an example of Positive Feedback System
In a positive feedback mechanism, the output of the system stimulates the system in such a way as to further increase the output. As a consequence it amplifies or magnifies a certain disturbance or activity, leading to an increase in magnitude. Positive feedback mechanisms control self-perpetuating events that can be out of control. This tends to move a system away from its equilibrium state and make it more unstable.

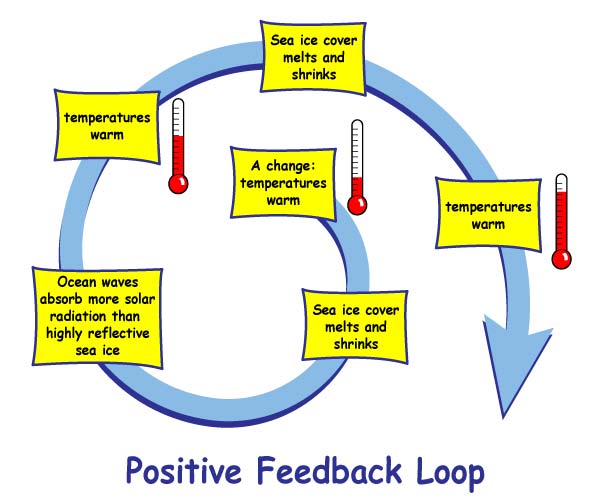
Characteristics
- Price Formation is distorted.
- Distortion in relative prices
- Misallocation of resources.
- Entrepreneurs get distorted signals about market demand. Impossibility of Economic Calculation
- Companies are funded by credit.
- High entry barriers for new providers.
- Projects risks is transferred to citizens
- Mismatches between supply and demand. Cantillon effects
- Values imposed by credit preferences.
Where we are?

| Feature | Negative | Positive | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decentralized | Centralized | Centralized | Decentralized | |
| Barter, Commodity, Metal | Representative | Fiat, Plastic | Crypto | |
| Price Formation | Distorted | |||
| Relative Prices | Distorted | |||
| Liquidity Available | Very Limited | Very Limited | ||
| Critical Resources | Possible | Possible | ||
| Allocation of Resources | Missallocation | |||
| Economic Calculation | Distorted | |||
| Credit Availability | No | No | ||
| Entry Barriers | Yes | |||
| Projects Risk | On Citizens | |||
| Supply / Demand matching | No | |||
| Externalities | Too Many | Too Many | ||
| Social Values | Imposed | |||
Privately Issued Currencies
Currency as a driver
A Society with Privately Issued Currencies is a return to the Negative Feedback System but solves the problem of this structure
- Hoarding won't cut liquidity
- Externalities can be fixed
- There are not Critical Resources
- No Money Scarcity
- Availability of Credit
Best of both worlds
- Daily poll on resource assignment. Investors and consumers, as cryptousers, decide on every action to whom assign productive resources based on their perception on the credibility of the issuer.
- Competence of money. Dislike centralized money issuing, when the money is issued by private parties in competence their relative value is proportional to the credibility of the issuer. This triggers the necessity for the issuer to boost credibility.
- Correct price formation. Investors translate to the coins the relative value that the perceive from the issuer. Consumers translate to the articles the relative value that they perceive in goods and services. Therefore, there is a correct price formation according to will of citizens.
- Relative prices prioritize consumers wishes
- Resources are allocated according to consumers wishes.
- Entrepreneurs get fair signals about market demand
- Private Investor assume the risk of their projects
- Companies are funded only by credit of investors.
- Little entry barriers for new providers.
- New demand is always satisfied by providers.
- Correct match demand/supply. Having the correct price formation for goods and services according to the will of citizens guarantees their supply matches exactly their expected demand without overpricing or undervalued mismatches of centralized money issuing. Let me social machine work on its own without bias.
- Values are freely chosen by citizens.
Not a new idea
